
Similarly, the observer on the left receives a longer wavelength, and hence he hears a lower frequency.

Because the observer on the right in case (b) receives a shorter wavelength, the frequency she receives must be higher. Thus, f multiplied by \(\lambda\) is a constant. The sound moves in a medium and has the same speed v in that medium whether the source is moving or not. My initial doubt was how the frequency and the. Now the Doppler effect shows us that if the source of the wave or the observer is in motion the frequency ( ) of the wave changes (Here I am talking about longitudinal waves propagating in a stationary medium).
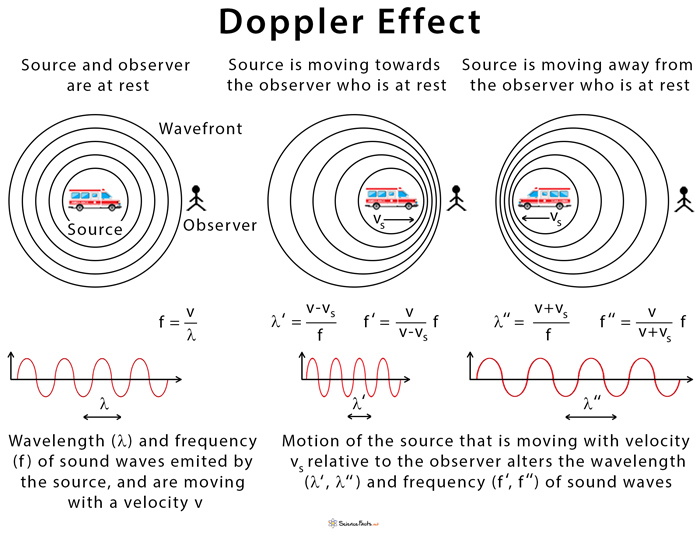
We know that wavelength and frequency are related by v = f\(\lambda\), where v is the fixed speed of sound. Also, velocity of propagation of a wave v. Motion away from the source decreases frequency as the observer on the left passes through fewer wave crests than he would if stationary. What is the Doppler Effect The Doppler effect is observed whenever the source of waves is moving with respect to an observer. The sound moves in a medium and has the same speed v. Motion toward the source increases frequency as the observer on the right passes through more wave crests than she would if stationary. We know that wavelength and frequency are related by vf, v f, where v is the fixed speed of sound. The Doppler effect causes a wave to be received with a frequency different from the one with which it is emitted as a result of the motion of the emitter and/or receiver. (c) The same effect is produced when the observers move relative to the source. The opposite is true for the observer on the left, where the wavelength is increased and the frequency is reduced. The wavelength is reduced, and consequently, the frequency is increased in the direction of motion, so that the observer on the right hears a higher-pitched sound. The Doppler effect is the change in frequency of a wave as the source moves relative to an observer, and explains why the pitch of a sound sometimes changes as it moves closer or further to or from an observer.
#DOPPLER EFFECT EQUATION VARIATONS HOW TO#
it explains how to solve doppler effect problems in.

(b) Sounds emitted by a source moving to the right spread out from the points at which they were emitted. This physics video tutorial provides a basic introduction into the doppler effect of moving sound waves. (a) When the source, observers, and air are stationary, the wavelength and frequency are the same in all directions and to all observers. We can use the Doppler effect equation to calculate both the velocity of the source and observer, the original frequency of the sound waves, and the observed. \):- Sounds emitted by a source spread out in spherical waves.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
